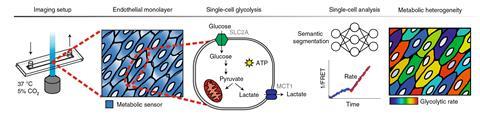
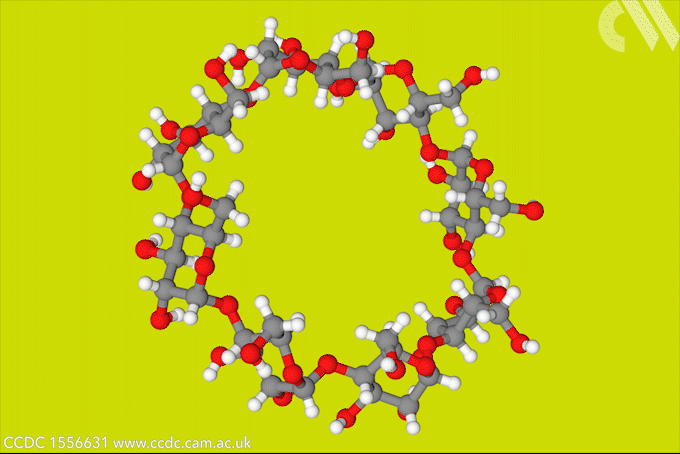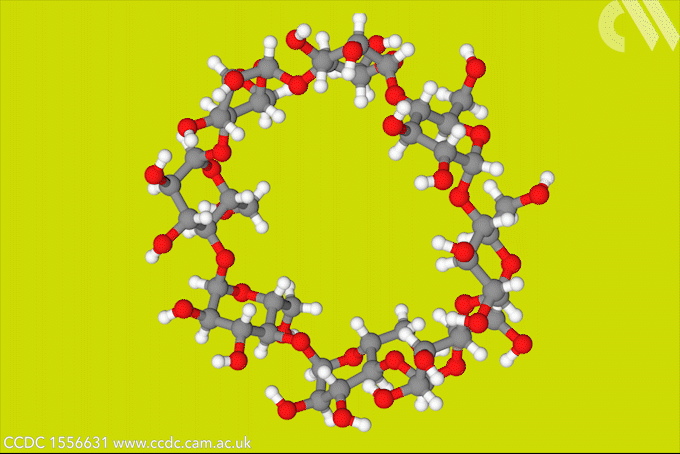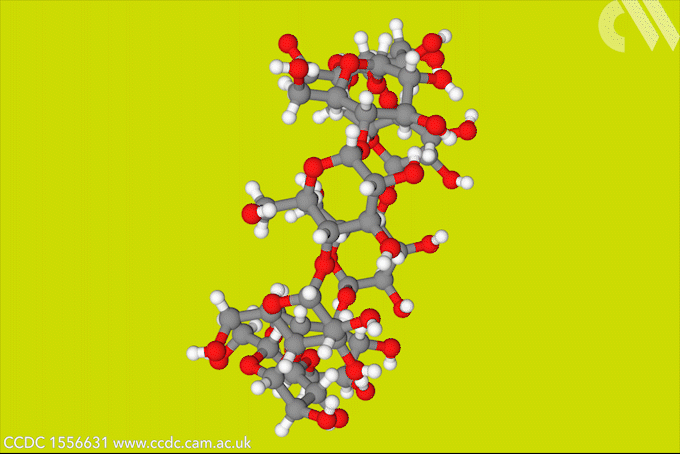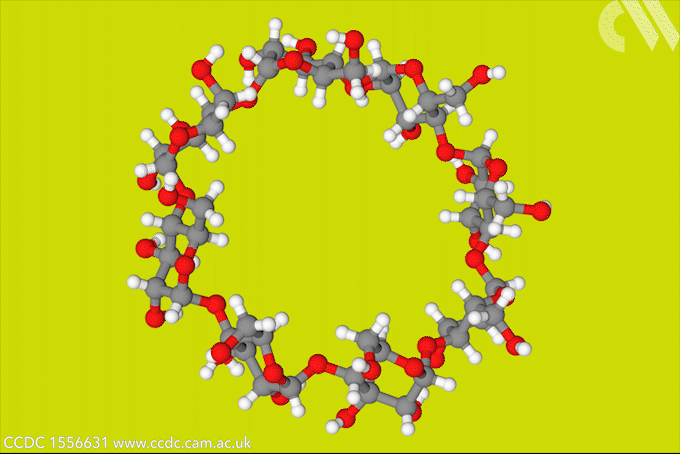
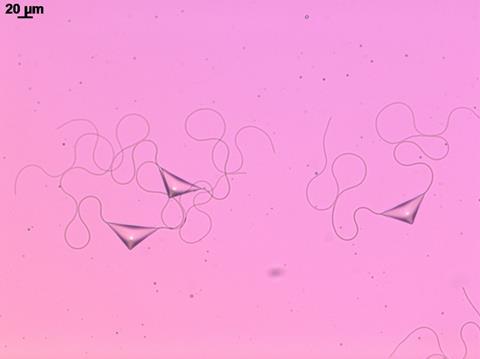
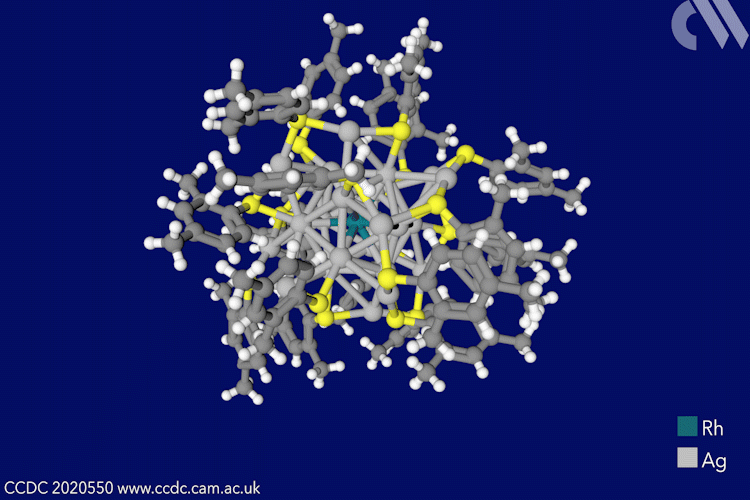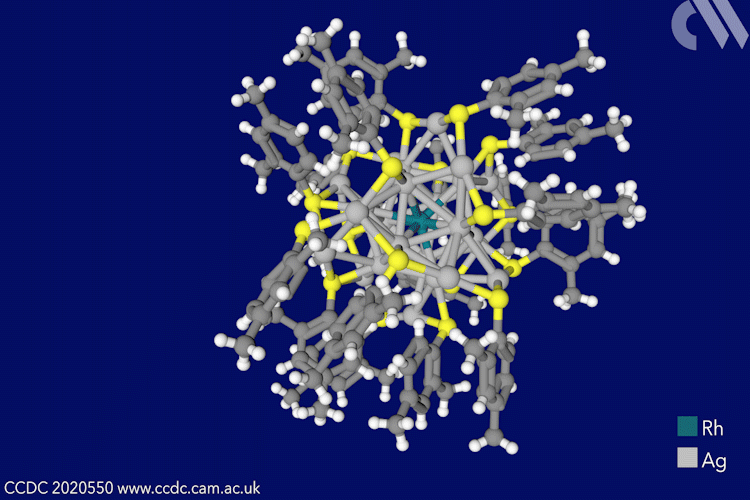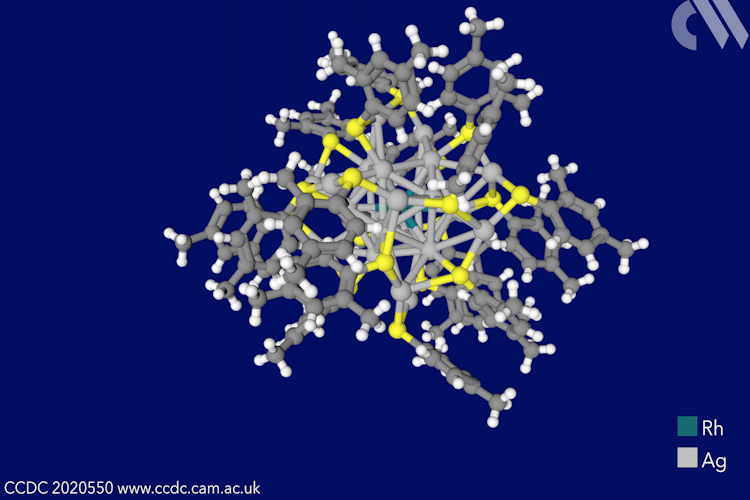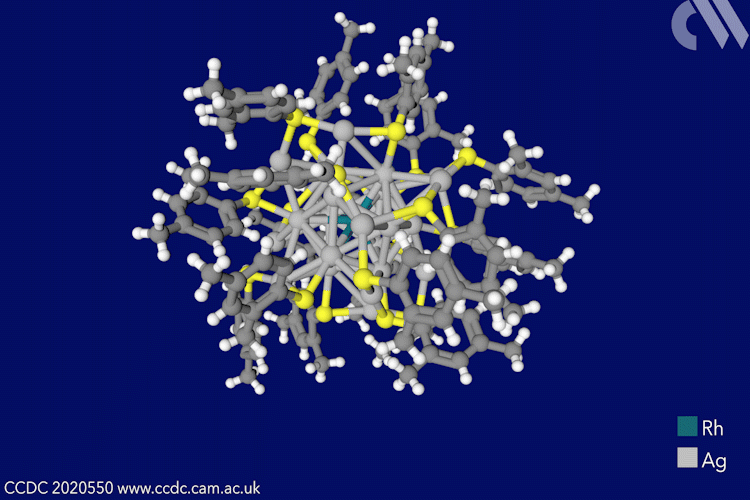
A gel that stops bleeding and sticks tissue together has been made using reptilase, an enzyme extracted from the venom of a pit viper. Visible light activates the bioadhesive, which also reduces bleeding by promoting blood clotting. Bioadhesives use chemical bonds or physical interactions between themselves and tissue to heal wounds. It’s important to prevent […]
Read More