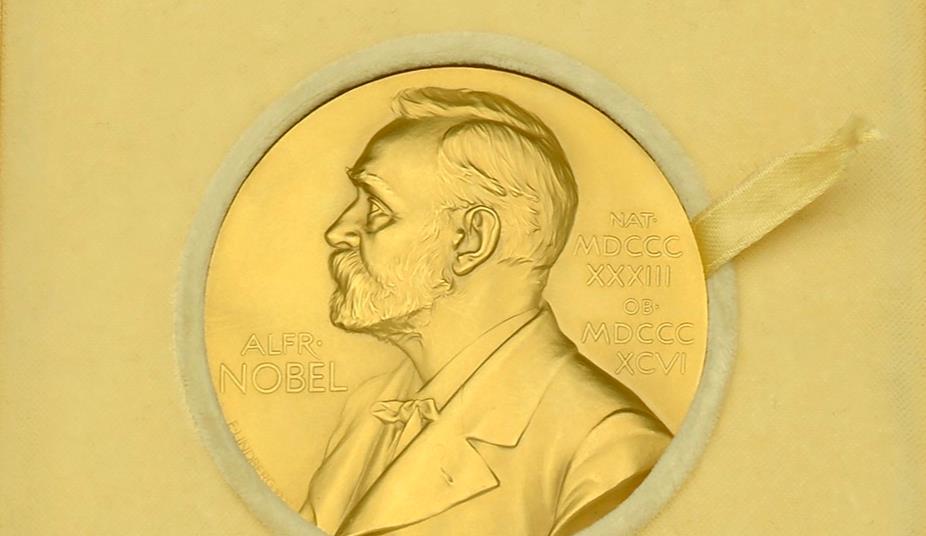
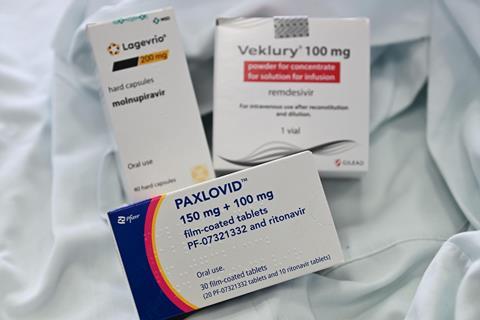
The Nobel prize medal awarded to British chemist Archer Martin in 1952, alongside Richard Synge for the invention of partition chromatography will be sold by his family via the London-based auctioneer Noonans on 2 February 2023. It is anticipated that the medal will bring in between £100,000 and £150,000. Martin’s road to the development of […]
Read More