In the seventeenth century, Marin Mersenne (1588–1648) was a very central and highly influential figure in the European intellectual and scientific communities; a man, who almost literally knew everybody and was known by everybody in those communities. Today, in the big names, big events, popular versions of the history of science he remains only known to specialist historian of science and also mathematicians, who have heard of Mersenne Primes, although most of those mathematicians probably have no idea, who this Mersenne guy actually was. So, who was Marin Mersenne and why does he deserve to be better known than he is?

Mersenne was born 8 September 1588, the son of Julien Mersenne and his wife Jeanne, simple peasants, in Moulière near Oizé, a small commune in the Pays de la Loire in North-Western France. He was first educated at the at the nearby College du Mans and then from 1604 to 1609 at the newly founded Jesuit Collège Henri-IV de La Flèche. The latter is important as in La Flèche he would have received the mathematical programme created by Christoph Clavius for the Jesuit schools and colleges, the best mathematical education available in Europe at the time. A fellow student at La Flèche was René Descartes (1596–1650) with whom he would become later in life close friends.
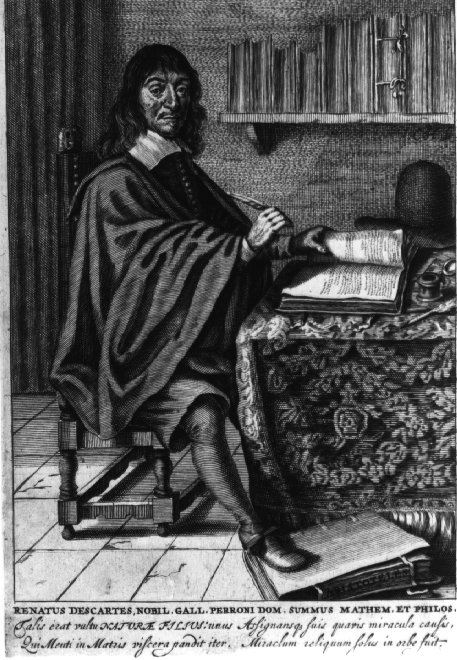

However, it is unlikely that they became friends then as Mersenne was eight years older. Leaving La Flèche he continued his education in Greek, Hebrew, and theology at the Collège Royal and the Sorbonne in Paris. In 1611 he became a Minim friar and a year later was ordained as a priest. The Minims are a mendicant order founded in Italy in the fifteenth century. From 1614 to 1618 he taught philosophy and theology at Nevers but was recalled to Paris in 1619 to the newly established house on the Place Royal (now Place des Vosges), where he remained, apart from travels through France, to Holland, and to Italy, until his death.
In Paris he was introduced to the intellectual elite by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Pereisc (1580–1637)–wealthy astronomer, antiquarian, and patron of science–whom he had got to know in 1616.

Settled in Paris, Mersenne began a career as a prolific author, both editing and publishing new editions of classical works and producing original volumes. In the 1620s his emphasis was on promoting and defending the Thomist, Aristotelian philosophy and theology in which he’d been educated. In his first book, Questiones celeberrimae in Genesim (1623),
he attacked those he saw as opponents of the true Catholic religion, Platonist, cabbalistic and hermetic authors such as Telesio, Pomponazzi, Bruno and Robert Fludd. His second book, L’impiété des déistes, athées, et libertins de ce temps (1624), continued his attacks on the propagators of magic and the occult. His third book, La Vérité des sciences (1625), attacks alchemists and sceptics and includes a compendium of texts over ancient and recent achievements in the mathematical sciences that he saw as in conformity with his Christian belief. The latter drew the attention of Pierre Gassendi (1592–1655), who became his closest friend. I shall return to their joint activities in Paris later but now turn to Mersenne’s own direct scientific contributions, which began to replace the earlier concentration on theology and philosophy.

Mersenne’s scientific interests lay in mathematics and in particular what Aristotle, who was not a fan of mathematics, claiming it did not apply to the real world, called the mixed sciences or mixed mathematics i.e., astronomy, optics, statics, etc. Here he compiled to collections of treatises on mixed mathematics, his Synopsis Mathematica (1626) and Universae geometriae synopsis (1644). In his Traité de l’Harmonie Universelle (1627), to which we will return, Mersenne gives a general introduction to his concept of the mathematical disciplines:
Geometry looks at continuous quantity, pure and deprived from matter and from everything which falls upon the senses; arithmetic contemplates discrete quantities, i.e. numbers; music concerns har- monic numbers, i.e. those numbers which are useful to the sound; cosmography contemplates the continuous quantity of the whole world; optics looks at it jointly with light rays; chronology talks about successive continuous quantity, i.e. past time; and mechanics concerns that quantity which is useful to machines, to the making of instruments and to anything that belongs to our works. Some also adds judiciary astrology. However, proofs of this discipline are borrowed either from astronomy (that I have comprised under cosmology) or from other sciences.
In optics he addressed the problem of spherical aberration in lenses and mirrors and suggested a series of twin mirror reflecting telescopes, which remained purely hypothetical and were never realised.
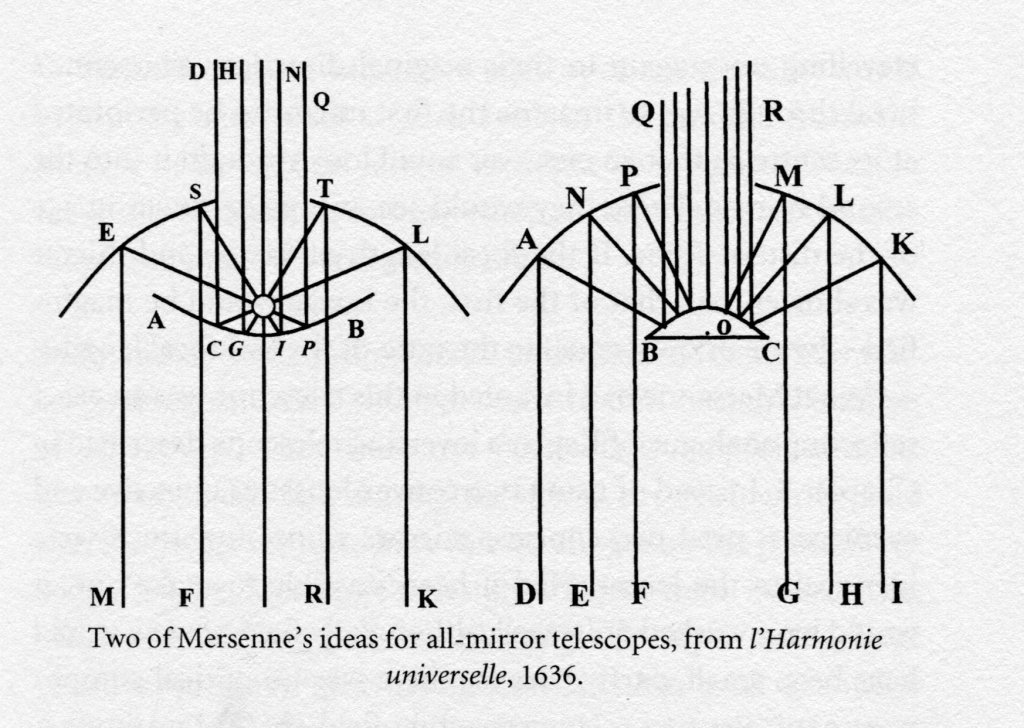
This is because they were heavily and falsely criticised by Descartes, who didn’t really understand them. It was Mersenne, who pushed Descartes to his solution of the refraction problem and the discovery of the sine law. He wrote three books on optics, De Natura lucis (1623); Opticae (1644); L’Optique et la catoptrique (1651). Although his theoretical reflecting telescopes were published in his Harmonie universelle (1636), see below.
Mersenne also wrote and published collections of essays on other areas of mixed mathematics, mechanics, pneumatics, hydro- statics, navigation, and weights and measures, Cogitata physico-mathematica (1644); Novarum observationum physico- mathematicarum tomus III (1647).
Mersenne dabbled a bit in mathematics itself but unlike many of his friends did not contribute much to pure mathematics except from the Mersenne prime numbers those which can be written in the form Mn = 2n − 1 for some integer n. This was his contribution to a long search by mathematicians for some form of law that consistently generates prime numbers. Mersenne’s law whilst generating some primes doesn’t consistently generate primes but it has been developed into its own small branch of mathematics.
It was, however, in the field of music, as the title quoted above would suggest, which had been considered as a branch of mathematics in the quadrivium since antiquity, and acoustics that Mersenne made his biggest contribution. This has led to him being labelled the “father of acoustics”, a label that long term readers of this blog will know that I reject, but one that does to some extent encapsulate his foundational contributions to the discipline. He wrote and published five books on the subject over a period of twenty years–Traité de l’harmonie universelle (1627); Questions harmoniques (1634); Les preludes de l’harmonie universelle (1634); Harmonie universelle (1636); Harmonicorum libri XII (1648)–of which his monumental (800 page) Harmonie universelle was the most important and most influential.

In this work Mersenne covers the full spectrum including the nature of sounds, movements, consonance, dissonance, genres, modes of composition, voice, singing, and all kinds of harmonic instruments. Of note is the fact that he looks at the articulation of sound by the human voice and not just the tones produced by instruments. He also twice tried to determine the speed of sound. The first time directly by measuring the elapse of time between observing the muzzle flash of a cannon and hearing the sound of the shot being fired. The value he determined 448 m/s was higher than the actual value of 342 m/s. In the second attempt, recorded in the Harmonie universelle (1636), he measured the time for the sound to echo back off a wall at a predetermined distance and recorded the value of 316 m/s. So, despite the primitive form of his experiment his values were certainly in the right range.
Mersenne also determined the correct formular for determining the frequency of a vibrating string, something that Galileo’s father Vincenzo (1520–1591) had worked on. This is now known as Mersenne’s Law and states that the frequency is inversely proportional to the length of the string, proportional to the square root of the stretching force, and inversely proportional to the square root of the mass per unit length.
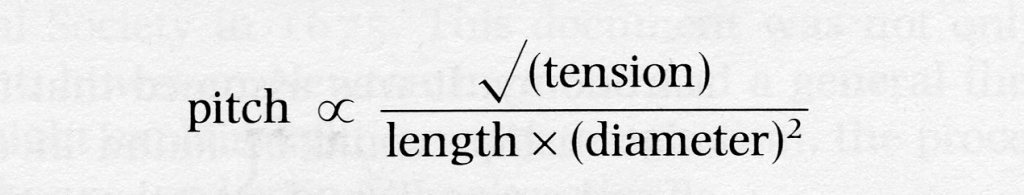
Vincenzo Galileo was also involved in a major debate about the correct size of the intervals on the musical scale, which was rumbling on in the late sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries. It was once again Mersenne, who produced the solution that we still use today.
Although Mersenne is certainly credited and honoured by acoustic researchers and music theorists for his discoveries in these areas, perhaps his most important contribution to the development of the sciences in the seventeenth century was as a networker and science communicator in a time when scientific journals didn’t exist yet.
Together with Gassendi he began to hold weekly meetings in his humble cell with other natural philosophers, mathematicians, and other intellectuals in Paris. Sometime after 1633 these meetings became weekly and took place in rotation in the houses of the participants and acquired the name Academia Parisiensis. The list of participants reads like an intellectual who’s who of seventeenth century Europe and included René Descartes, Étienne Pascal and his son Blaise, Gilles de Roberville, Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Pereisc, Pierre de Fermat, Claude Mydorge, the English contigent, Thomas Hobbes, Kenhelm Digby, and the Cavendishes, and for those not living in or near Paris such as Isaac Beeckman, Jan Baptist van Helmont, Constantijn Huygens and his son Christiaan, and not least Galileo Galilei by correspondence. When he died approximately six hundred letters were found in his cell from seventy-nine different correspondents. In total 193 scholars and literati have been identified as participants. Here it should be noted that although he tended to reject the new emerging sciences in his earlier defence of Thomist philosophy, he now embraced it as compatible with his teology and began to promote it.
This academy filled a similar function to the Gresham College group and Hartlib Circle in England, as well as other groups in other lands, as precursors to the more formal scientific academies such as the Académie des sciences in Paris and the Royal Society in London. There is evidence that Jean-Baptist Colbert (1619–1683), the French Minister of State, modelled his Académie des sciences on the Academia Parisiensis. Like its formal successors the Academia Parisiensis served as a forum for scholars to exchange views and theories and discuss each other’s work. Mersenne’s aim in establishing this forum was to stimulate cooperation between the participants believing science to be best followed as a collective enterprise.
Mersenne’s role was not restricted to that of convener, but he functioned as a sort of agent provocateur deliberately stimulating participants to take up research programmes that he inaugurated. For example, he brought Torricelli’s primitive barometer to Paris and introduced it to the Pascals. It is thought that he initiated the idea to send Blaise Pascal’s brother-in-law up the Puy de Dôme to measure the decreasing atmospheric pressure.
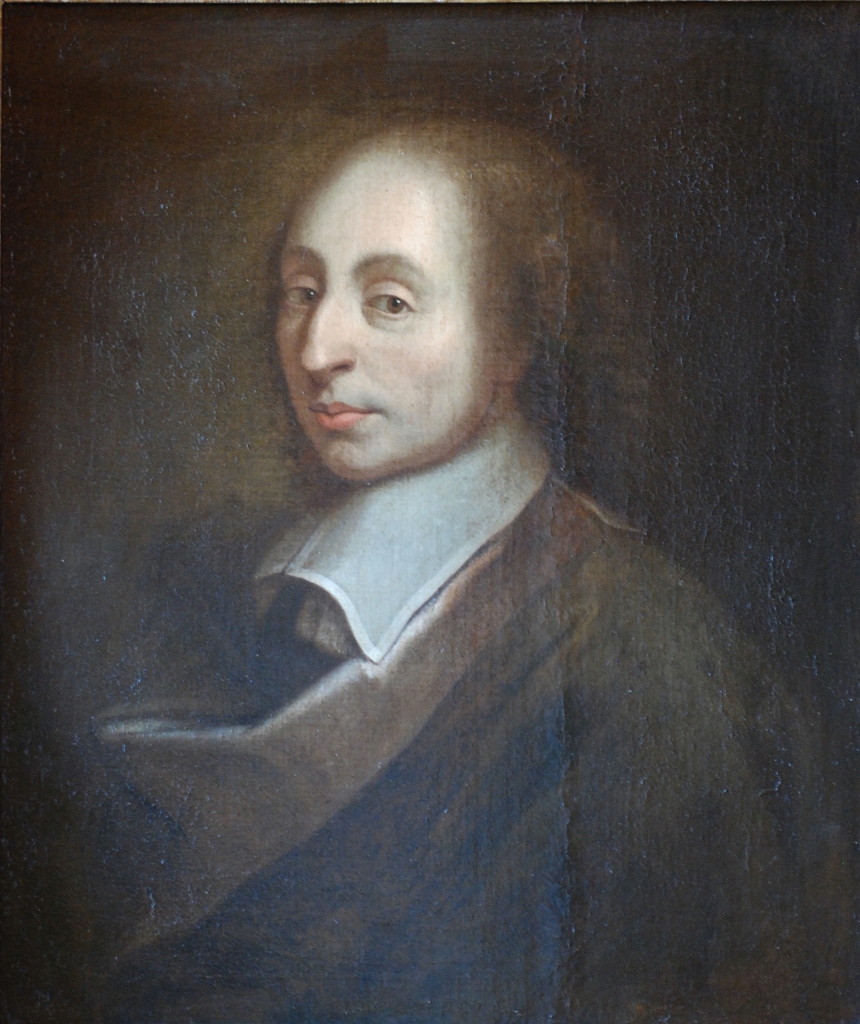

Although they never met and only corresponded, he introduced Christiaan Huygens to the concept of using a pendulum to measure time, leading to Huygens’ invention of the pendulum clock.
<br />
*oil on paper on panel<br />
*30 x 24 cm<br />
*signed b.l.: C.Netscher / 1671</p>
<p> ” data-medium-file=”https://wolfscientific.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/musical-mathematical-minim-marin-mersenne-38.jpg” data-large-file=”https://thonyc.files.wordpress.com/2021/09/christiaan_huygens-painting.jpeg?w=500″ src=”https://wolfscientific.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/musical-mathematical-minim-marin-mersenne-8.jpg” alt class=”wp-image-7874″ srcset=”https://wolfscientific.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/musical-mathematical-minim-marin-mersenne-8.jpg 781w, https://wolfscientific.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/musical-mathematical-minim-marin-mersenne-36.jpg 1562w, https://wolfscientific.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/musical-mathematical-minim-marin-mersenne-37.jpg 114w, https://wolfscientific.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/musical-mathematical-minim-marin-mersenne-38.jpg 229w, https://wolfscientific.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/musical-mathematical-minim-marin-mersenne-39.jpg 768w” sizes=”(max-width: 781px) 100vw, 781px”></a><figcaption>Portrait of Christiaan Huygens (1629-1695) C.Netscher / 1671 Source: Wikimedia Commons</figcaption></figure>
<p>It was Mersenne, who brought the still very young Blaise Pascal together with René Descartes, with the hope that the brilliant mathematicians would cooperate, in this case he failed. In fact, the two later became opponents divided by their conflicting religious views. Mersenne also expended a lot of effort promoting the work of Galileo to others in his group, even offering to translate and publish Galileo’s work in French, an offer that the Tuscan mathematician declined. He did, however, publish an unpublished text by Galileo on mechanics, <em>Les Mechaniques de Galilée</em>.</p>
<p>Although not the author of a big theory or big idea, or the instigators of a big event, Mersenne actually contributed with his activities at least as much, if not more, to the development of science in the seventeenth century as any of the more famous big names. If we really want to understand how science develops then we need to pay more attention to figures like Mersenne and turn down the volume on the big names. </p>
</div><!-- .entry-content -->
</article> <!-- /.blog-single -->
<nav class=)