**Exercise and Metformin: Understanding the Intricate Relationship in Diabetes Prevention**
Exercise is highly regarded for its contribution to diabetes prevention, improving cardiovascular health, and promoting overall wellness. Concurrently, metformin, a commonly prescribed diabetes treatment, plays a significant role in controlling blood glucose levels for millions globally. Nevertheless, recent research from Rutgers University has expressed concerns about the interaction between these two effective approaches.
**Study Overview**
The clinical trial, detailed in *The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism*, involved 72 adults at risk for metabolic syndrome. Participants were assigned to either high- or low-intensity exercise while receiving either metformin or a placebo over a period of 16 weeks. The researchers examined blood vessel function, aerobic fitness, and glucose regulation—crucial metrics of diabetes risk and cardiovascular health.
**Findings**
Results indicated that exercise on its own enhanced vascular insulin sensitivity, boosting blood circulation and glucose uptake in muscle tissues. However, when metformin was included, these advantages showed a marked decline. The medication also reduced enhancements in aerobic capacity and mitigated positive shifts in inflammation and fasting glucose levels.
Lead author Steven Malin stated that these results challenge the prevailing belief that exercise paired with metformin leads to greater benefits.
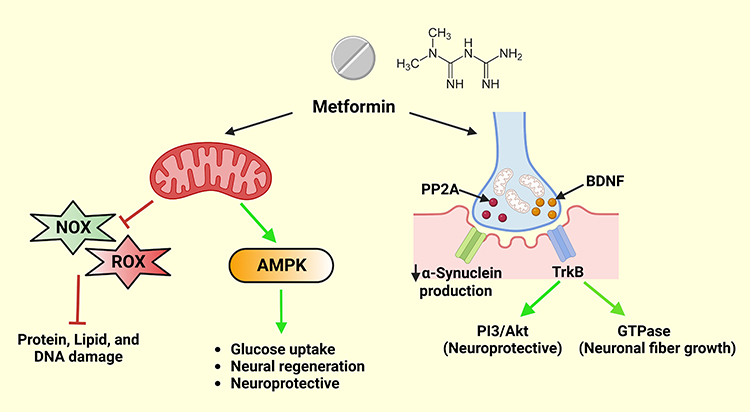
**Potential Mechanism**
The disruption may arise from metformin’s action at the cellular level. Although it lowers blood glucose by modifying mitochondrial function and curbing oxidative stress, these mitochondria are critical for adapting to the demands of physical activity, supporting improvements in muscle and cardiovascular health.
**Implications**
This interaction suggests a potential concern for those dependent on both exercise and metformin, as they might not gain the full anticipated advantages. The research emphasizes that while these results are important, they should not discourage individuals from pursuing either exercise or metformin. Rather, it underscores the need for more refined medical counsel regarding their combined application.
**Call to Action**
With a considerable segment of the population impacted by type 2 diabetes, grasping how medications and lifestyle changes intersect is vital for effective management and prevention of the disease. Continued research and enhanced guidance are essential for maximizing the dual benefits of pharmacological and lifestyle strategies, guaranteeing that individuals receive thorough care.
For further reading, refer to the study at DOI: [10.1210/clinem/dgaf551](https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgaf551).