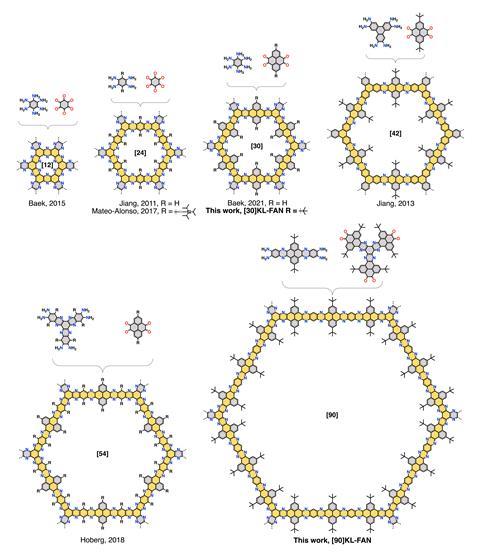
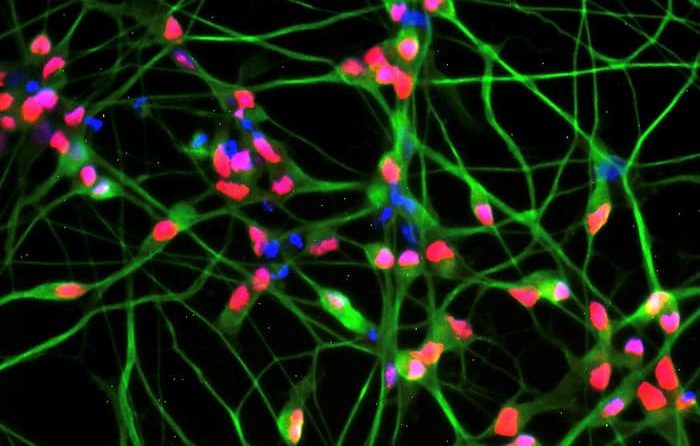
Chemists have made the biggest network structure of its kind, a giant hexagon made out of 90 fused aromatic rings. This is almost double the size of the previous record holder, a 54-ring structure reported in 2018. Fused aromatic networks (Fans) are a more chemically diverse alternative to perforated graphene. As the flat honeycomb structures […]
Read More